Moderate Dehydration Fluid Replacement Made Simple

Medically reviewed by Micaela Strevay, FNP-C, PMHNP-BC
Table of Contents
How to Recognize Moderate Dehydration

When it comes to moderate dehydration fluid replacement , quick action is crucial. Moderate dehydration means your body has lost a significant amount of water—between 6% to 10% of your body weight—which can impact how your body functions.
Here’s a quick overview:
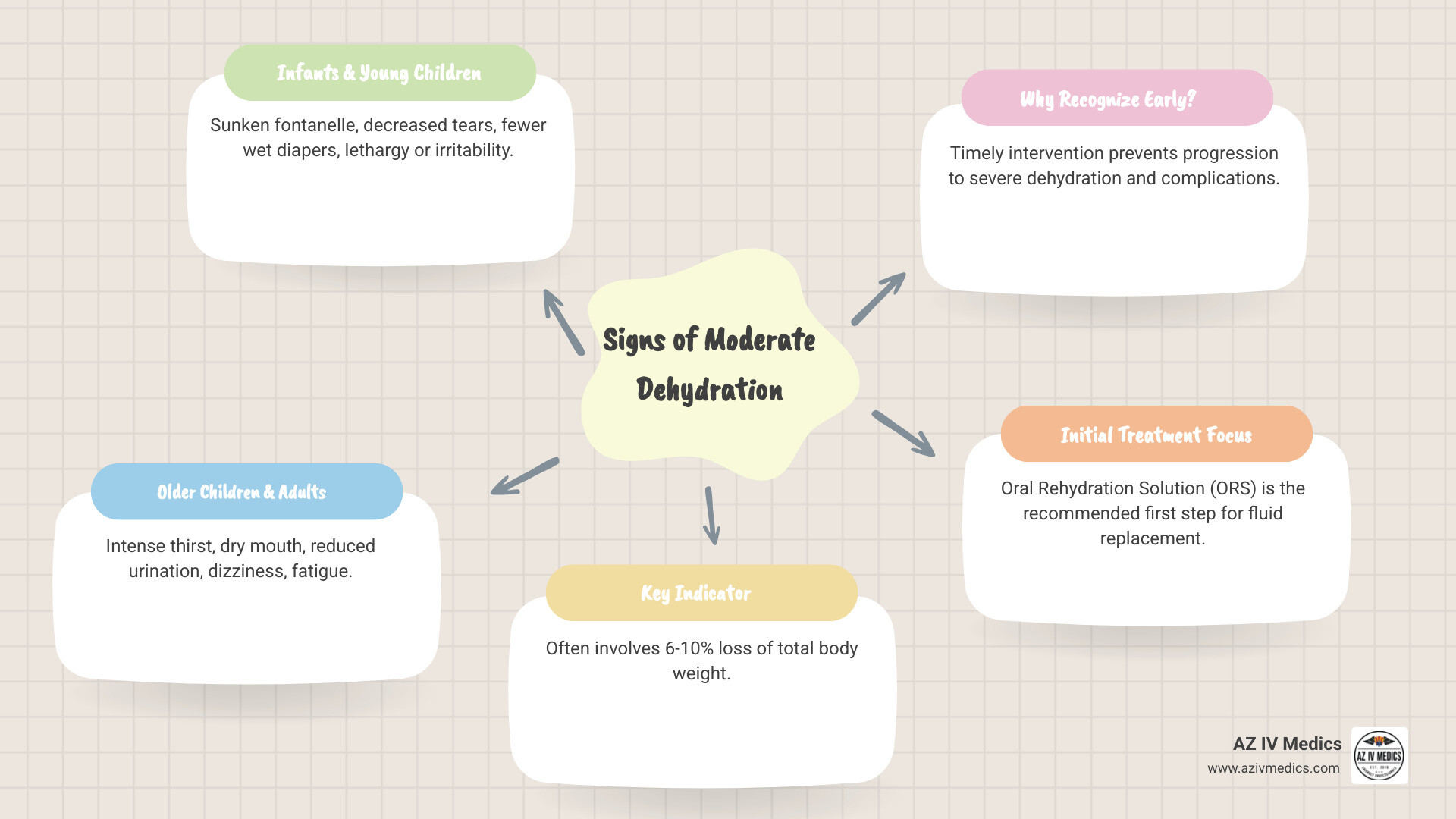
- Infants & Young Children: A 10% loss of body fluid. Signs include decreased tears, a sunken soft spot, or fewer wet diapers.
- Older Children & Adults: A 6% to 10% loss of body fluid. You might notice intense thirst, dry mouth, reduced urination, or dizziness.
- Primary Treatment: Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) is the best first step to replace lost water and electrolytes.
Understanding these signs prevents the condition from worsening. This guide covers how to recognize moderate dehydration and the best ways to replace lost fluids.
As Joseph Lopez AZIVM, my work in mobile IV therapy has shown me the impact of moderate dehydration fluid replacement on quick recovery. I'm dedicated to finding effective solutions for rapid relief.
Explore more about moderate dehydration fluid replacement :
Recognizing the need for moderate dehydration fluid replacement begins with a clinical assessment of signs and symptoms, not just thirst. While mild dehydration has subtle cues, moderate dehydration brings more noticeable indicators. Scientific research on clinical dehydration scales highlights that specific signs help gauge the severity of fluid loss.

Signs in Infants and Young Children
Infants and young children are especially vulnerable. For them, moderate dehydration fluid replacement is critical when you see:
- Sunken fontanelle: The soft spot on a baby's head appears depressed.
- Decreased tears: Crying without tears is a classic sign.
- Reduced wet diapers: Fewer than usual, or no wet diapers for several hours.
- Lethargy or irritability: Unusually sleepy, listless, or fussy.
- Cool extremities: Hands and feet might feel cool to the touch.
- Tachycardia: An liftd heart rate.
- 6-10% body weight loss: The clinical benchmark for moderate dehydration in this age group.
These signs, especially in combination, warrant immediate attention.
Signs in Older Children and Adults
For older children and adults, the signs of moderate dehydration are more apparent. Their intensity and persistence are key indicators for moderate dehydration fluid replacement :
- Thirst: A strong, persistent feeling of thirst.
- Dry mouth: Your mouth and tongue might feel sticky or parched.
- Reduced urination: Less frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Dark-colored urine: Urine will appear darker than usual.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or lacking energy.
- Dizziness: Lightheadedness, especially when standing up quickly.
- Sunken eyes: Eyes might appear hollow or sunken.
- 6-10% body weight loss: The clinical definition for moderate dehydration in adults.

If you're experiencing these symptoms, it's a clear signal that your body needs significant fluid intervention.
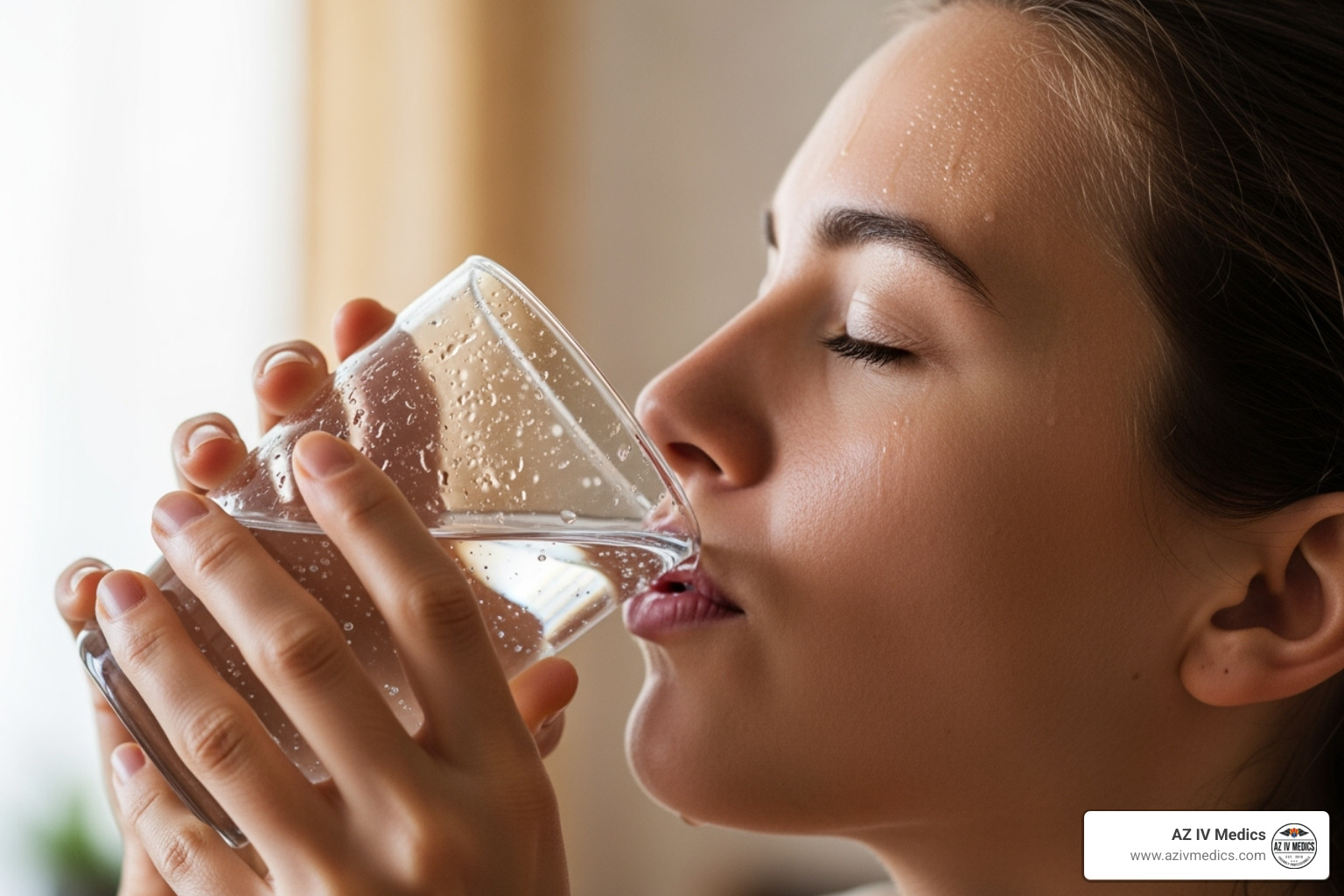
The First Step: Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT)
For many cases of moderate dehydration fluid replacement , the first and most effective step is Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT). Endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), ORT is the first-line treatment for mild to moderate dehydration because it's gentle, non-invasive, and works quickly.
ORT involves drinking an Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS), a precisely balanced mix of water, salts, and sugar. This isn't just water; the glucose (sugar) in ORS helps the small intestine absorb sodium, and water follows, allowing for rapid and efficient rehydration. This makes ORS far more effective than plain water or sugary drinks.
We use ORT for mild to moderate dehydration when a person can drink fluids without excessive vomiting. It's ideal for situations like:
- Gastroenteritis (stomach flu) with vomiting and diarrhea.
- Excessive sweating from exercise, heat, or fever.
- Persistent thirst and fatigue from fluid deficit.
Key Components and Administration of ORS
The effectiveness of ORS lies in its key components for moderate dehydration fluid replacement :
- Glucose (sugar): Crucial for helping the body absorb sodium and water.
- Sodium: An essential electrolyte lost during dehydration that helps get water into your cells.
- Potassium: A vital electrolyte depleted by vomiting or diarrhea.
For ORS to work, proper administration is key. If using a powder, mix it exactly according to package directions with clean water. Imprecise mixing can make it less effective or even harmful.
Drink the solution in small, frequent sips to avoid upsetting your stomach. Chugging large amounts can lead to more vomiting. For moderate dehydration, a general guideline for adults and older children is 100 mL of ORS per kilogram of body weight over the first 4 hours . For younger children, an additional 50-100 mL of ORS is often recommended after each episode of vomiting or diarrhea.
The effectiveness of ORT is well-established. A meta-analysis on ORT vs IV therapy found it highly effective, often comparable to IV therapy for moderate dehydration, especially in children. Studies show that fewer than 5% of children treated with ORT require IV fluids, highlighting its success!
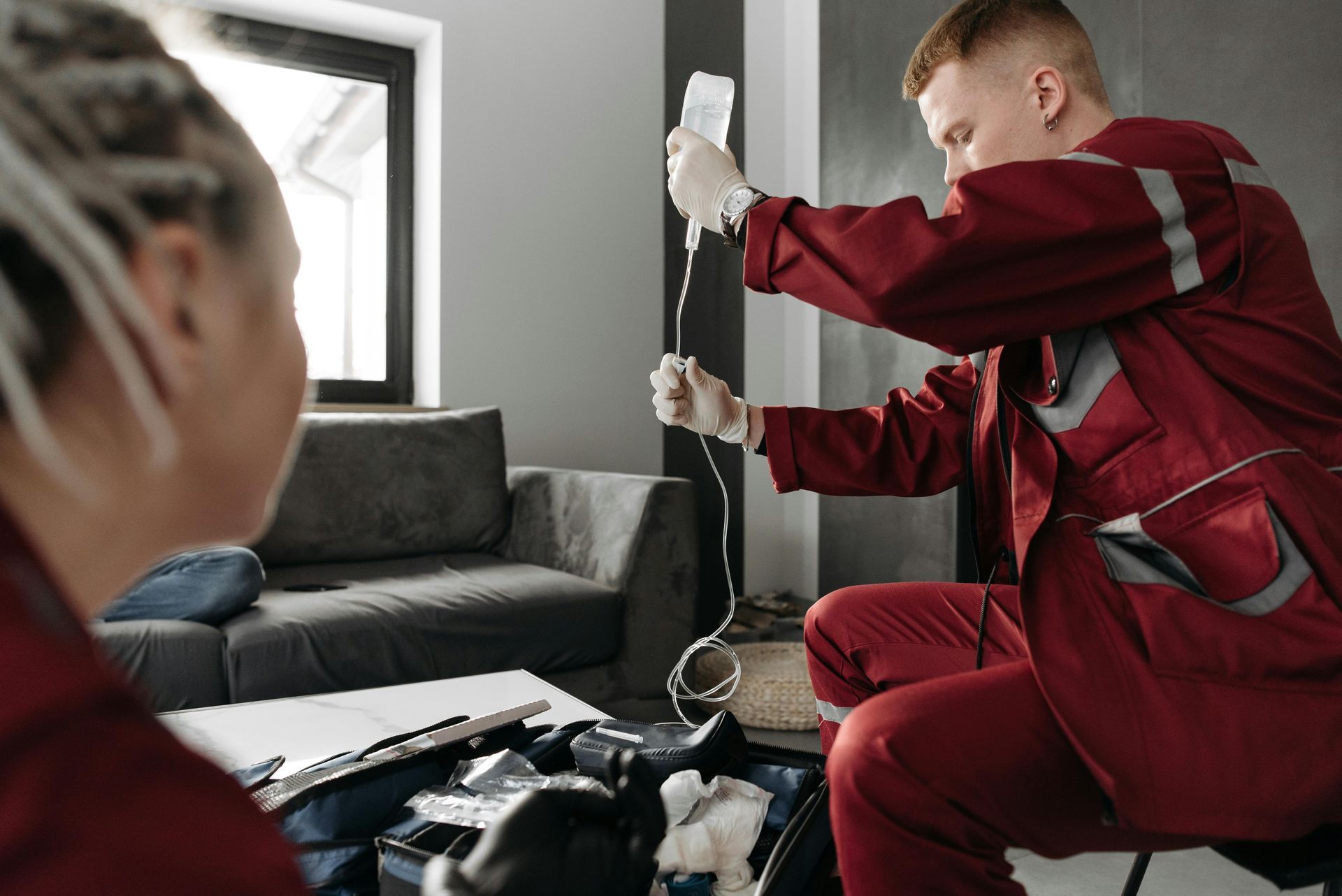
When to Escalate: IV Fluid Replacement for Moderate Dehydration
While Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT) is the first choice for moderate dehydration, sometimes IV therapy is necessary. IV therapy delivers fluids and electrolytes directly into the bloodstream for rapid rehydration when oral fluids aren't enough.
When is IV Therapy Necessary?
For moderate dehydration fluid replacement , IV therapy is considered when a person experiences:
- Persistent vomiting: Inability to keep any oral fluids down.
- Altered mental status: Confusion, extreme sleepiness, or unresponsiveness.
- Signs of shock: A very fast heart rate, low blood pressure, or cold, clammy skin.
- Failure of ORT: Symptoms do not improve or worsen despite trying ORT.
- Rapid deterioration: Signs of severe dehydration appear quickly.
- Underlying medical conditions: Health issues like kidney disease can complicate fluid balance.
Seek emergency care immediately for signs like confusion, extreme sluggishness, very low blood pressure, or a lack of urination for many hours.
This is where services like AZ IV Medics can help. While severe dehydration requires an ER visit, our mobile IV therapy is a game-changer for moderate cases where oral fluids fail. We bring treatment to you in Phoenix, Tucson, Scottsdale, Mesa, or Flagstaff, offering quick relief without the wait.
Calculating and Choosing IV Fluids
Healthcare professionals carefully calculate the amount of fluid needed for moderate dehydration fluid replacement . This calculation considers three parts:
- Fluid Deficit: The amount of fluid already lost, estimated from weight loss.
- Maintenance Needs: The daily fluid required for normal body functions.
- Ongoing Losses: Replacement for fluids still being lost from vomiting or diarrhea.
The total fluid is typically replaced over 24-48 hours. Clinical guidelines on maintenance IV fluids in children emphasize the importance of precise calculations to avoid complications.
For moderate dehydration fluid replacement , we use isotonic crystalloid solutions, which have a salt concentration similar to blood. This helps rehydrate you without causing major fluid shifts in your cells.
- Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl): A common choice that quickly boosts fluid volume and replaces sodium.
- Lactated Ringer's solution: Contains an electrolyte mix similar to blood plasma.
Dextrose (sugar) may be added for energy, and potassium may be added to replace losses, but only after confirming normal kidney function (i.e., you are urinating). Hypotonic solutions are generally avoided, especially in children, as they can cause cells to swell, leading to dangerous complications like cerebral edema.
Monitoring and Special Considerations
Administering fluids for moderate dehydration fluid replacement is the first step, but continuous monitoring is essential to ensure the treatment is working safely and effectively. This allows us to track your recovery and prevent potential problems.

Essential Monitoring During Treatment
During fluid replacement, our team closely monitors key indicators to track your progress:
- Vital Signs: We check for a normalizing heart rate and blood pressure.
- Urine Output: An increase in urine production and a lighter color are good signs of rehydration.
- Body Weight: A gradual weight gain indicates successful fluid replacement.
- Mental Status: We look for improved alertness and responsiveness.
- Capillary Refill: A quick return of color to a nail bed (less than 3 seconds) shows improved circulation.
- Serum Electrolytes: Blood tests may be used to ensure minerals like sodium and potassium are returning to healthy levels.
Potential Complications and Special Cases
While our goal is to rehydrate you, we are also vigilant about preventing complications. Our team is trained to spot these risks early.
- Fluid Overload: Giving too much fluid too quickly can cause swelling ( edema ) or difficulty breathing ( pulmonary edema ). Careful administration prevents this.
- Cerebral Edema: Brain swelling is a rare but serious risk, which is why we carefully choose fluids and infusion rates to ensure gentle rehydration.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Monitoring helps us prevent sodium levels from becoming too low ( hyponatremia ) or too high ( hypernatremia ).
- IV Access Complications: We watch for minor issues like bruising or rare complications like infection or vein inflammation ( phlebitis ).
Special considerations are crucial for patients with conditions like heart failure or kidney disease . Their fluid management requires extra precision to avoid overwhelming their systems. A thorough medical assessment is always our first step before starting moderate dehydration fluid replacement therapy.
Frequently Asked Questions about Moderate Dehydration
Here are answers to common questions about moderate dehydration fluid replacement .
Can I use sports drinks or juice instead of an Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS)?
For clinical dehydration from illness, the answer is generally no . While sports drinks and juices contain fluids, they are not ideal for moderate dehydration fluid replacement for two main reasons:
- Too much sugar: High sugar content can worsen diarrhea by drawing water into the intestines.
- Wrong electrolyte balance: They lack the correct ratio of sodium and potassium needed for effective rehydration during illness.
An ORS is specifically formulated with the optimal balance of glucose, sodium, and potassium for rehydration. While a diluted sports drink might be acceptable for mild dehydration after exercise, an ORS is the superior choice for illness-related dehydration, especially in children.
How long does it take to recover from moderate dehydration with treatment?
Recovery time for moderate dehydration fluid replacement depends on the severity, the cause, and how quickly treatment begins.
- Initial Rehydration (4-6 hours): With ORS, most people feel significantly better within 4 to 6 hours as their initial fluid deficit is corrected.
- Maintenance Phase: After the initial phase, it's crucial to continue drinking fluids to meet daily needs and replace any ongoing losses from vomiting or diarrhea. This continues until you are back to normal.
Recovery speed is influenced by the initial level of dehydration and adherence to the rehydration plan. It's important to keep hydrating even after you start to feel better.
What is the difference between dehydration and hypovolemia?
These terms are related but distinct.
- Dehydration: Refers to a loss of total body water , affecting fluid both inside and outside your cells.
- Hypovolemia: Specifically refers to a loss of fluid volume within your blood vessels (intravascular volume).
While severe dehydration causes hypovolemia, the terms are not interchangeable. For example, significant blood loss causes hypovolemia without dehydration. The distinction helps clinicians tailor treatment. For most cases of moderate dehydration fluid replacement , treating the dehydration also resolves the associated hypovolemia.
Conclusion
Navigating moderate dehydration fluid replacement is about recognizing the signs and responding appropriately. Spotting indicators like intense thirst, dry mouth, and reduced urination early is the first step toward recovery.
For most cases, Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT) is a simple, effective solution that replenishes fluids and electrolytes. However, when ORT isn't enough due to persistent symptoms or vomiting, intravenous (IV) fluid therapy offers rapid rehydration. Healthcare professionals ensure IV fluids are administered safely and effectively, with careful calculations and monitoring.
While this guide is informative, always seek professional medical care for severe dehydration or if you are unsure about your symptoms.
For convenient moderate dehydration fluid replacement without the wait, AZ IV Medics is here to help. We deliver mobile IV hydration and wellness treatments to your door in Phoenix, Tucson, Scottsdale, Mesa, and Flagstaff, making your path to rehydration comfortable and seamless.
Explore our mobile IV hydration services to learn how we can help you feel refreshed and revitalized. Stay hydrated and listen to your body.